The Chechnya Revolt: A Brief History and Ongoing Conflict
Introduction:
Chechnya is a republic located in the North Caucasus region of Russia. The Chechnya Revolt was a conflict between the Russian Federation and Chechen separatists seeking to gain independence and political autonomy. The conflict has continued for decades, leading to significant human rights violations and suffering for the people of Chechnya. This article aims to provide background information on the Chechnya revolt and its ongoing impact.
The Chechnya Revolt: A Brief History:
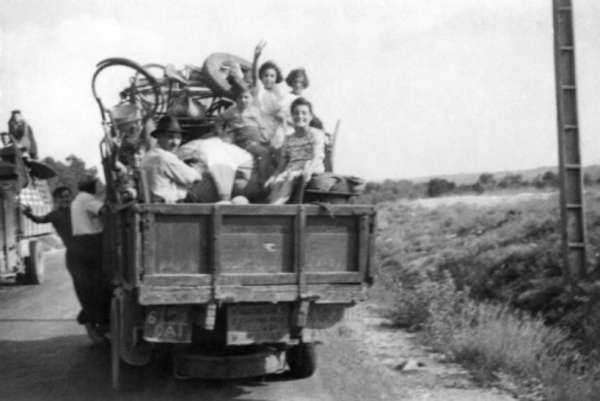
The Chechnya revolt began in the early 1990s after the fall of the Soviet Union. At the height of the conflict, the separatist forces controlled most of Chechnya, turning the region into a de facto independent state. However, in 1994, the Russian Federation invaded Chechnya, leading to a bloody conflict that lasted for several years, causing many civilian casualties and internally displacing thousands of people. The two parties signed a peace agreement in 1996, leading to a ceasefire, but this was short-lived as the conflict reignited in the early 2000s.
Ongoing Conflict:
The ongoing conflict in Chechnya continues to concern many human rights activists. The Chechen authorities have been accused of extrajudicial killings, enforced disappearances, and the torture of political dissidents and individuals perceived to be gay. Homosexuality is considered a taboo topic in Chechen society, and the reported detention, torture, and even murder of gay men in Chechnya have drawn significant international condemnation.
Recently, the Russian Federal Government has taken measures to assert control over the Chechen Republic. In 2019, the Russian government dissolved the previous constitution and replaced it with a new one, strengthening the president’s power. This has led to concerns about increased authoritarianism and further violations of human rights.
International Response:
Many international human rights organizations, such as Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch, have criticized the Russian government for its handling of the conflict in Chechnya. The European Court of Human Rights has also ruled against the Russian government, claiming multiple violations of human rights in Chechnya, including torture, abductions, and extrajudicial killings.
However, Russia has rejected such criticisms, arguing that it is fighting against terrorism and separatism in Chechnya. Additionally, the Russian government has claimed that it has made significant economic and infrastructure improvements in Chechnya.
Conclusion:
The Chechnya revolt is an ongoing conflict that continues to have significant humanitarian implications for the people of Chechnya. The Russian government’s attempts to suppress separatist movements have led to allegations of human rights violations and concerns about the erosion of democratic institutions. It is crucial that all parties involved work towards a peaceful resolution to the conflict, maintaining a commitment to human rights and upholding international law.
Chechnya, now situated within Russian Federation borders along with Georgia, is somewhat protected from outside enemies and other impeding influences by the Caucasus Mountains that surround them. Its history, though, includes the threat of Russian domination. This stemmed from the early nineteenth century, following the arrest, exile, and execution of Chechen leaders who had violated Chechnya human rights, that which piqued interest among Soviet authorities.